COE428 Lab 4: State Machine
1. IMPORTANT: Two week lab
Note that you have two weeks to complete this lab. This lab must be submitted at least 48 hours before the beginning of your
next lab period.
2. Prelab
preparation
Before coming to the lab you should:
· Read the lab. Try to prepare any questions you may have about the lab.
· Refer to Lab Guide.
·
Create
your lab directory for lab4. (i.e. use mkdir lab4 within your coe428
directory.)
·
Change
to your coe428/lab4 and unzip the lab4.zip file with the command:
unzip /home/courses/coe428/lab4/lab4.zip - Ensure that you have downloaded
properly by entering the command: make
No errors should be reported.
- Get a custom version of the
State Machine you are supposed to implement with the command /home/courses/coe428/bin/getLab4
|
Note |
|
The command /home/courses/coe428/bin/getLab4 will execute properly only on a
Sun Workstation. If you are using a computer other than a Sun workstation, please
ssh to a Sun Workstation. (For example, ssh genesis.ee.ryerson.ca) |
3.
Requirements
The requirements to
complete the lab are summarized below.
1.
Draw a
diagram of your state machine.
2.
Create an
executable program simState (based on C source code) that is
able to respond to the commands described below.
3.
Your
program will be presented with zero or more commands from stdin (each on
a line by itself) and must respond precisely as specified for each command as
listed below.
No Commands:
Before any commands are
issued to your program, it should print out the starting state.
One/Zero Commands:
These commands (a `0' or
a `1' on a line by itself) must print to stdout the name of the next
state given the supplied input, and update the current state.
Change command:
The change command is invoked by the letter `c' followed by a `1' or a `0' followed by the
name of a state (i.e. a single letter in the range A–H). This command modifies
the state machine such that the `0' (or `1') command applied to the current
state will cause the machine to change to the named state and that this change
is the state machine configuration will continue. This command should produce
no output.
Print command:
The print command is invoked with the single letter `p'. It should print to stdout the
state machine configuration as currently specified (i.e. including changes that
may have been made with change commands) in the same
format that your state machine was specified with.
Garbage Identify
command:
This command is invoked
with the single letter `g'. It should identify all states that are reachable or
unreachable from the current state. It always produces output to stdout.
If all states are
reachable, it should output No garbage. Otherwise, it should
output
Garbage: <unreachable states> where <unreachable states> is
the list of the state names that are no longer reachable.
Delete command:
This command is invoked
with `d', optionally followed by the name of a state to delete. When the ‘d’
command is invoked without the optional argument, it should delete (i.e. mark
as “deleted”) all un-deleted states that are unreachable. If there are no such
unreachable un-deleted states, it should print:
|
No states deleted. |
Otherwise, it should
print the message:
|
Deleted: <list of deleted states> |
If the ‘d’ command is
followed by an argument that it the valid name of a state, it should print out
either the message:
|
Deleted. |
if the state is not reachable and not already deleted. Otherwise, it
should print out the message:
|
Not deleted. |
If a state is
successfully deleted, it should no longer appear in the list of states produced
by the print command and it should be disallowed
as a final argument to the change command.
4.
Example
The description of a
state machine is given in a text file where each line has the following format:
|
<StateName>
<NextState0> <NextState1> |
The <StateName>
is the name of the state being defined, <NextState0> is the
name of next state if the input is `0'; and <NextState1> is the
name of next state if the input is `1'. All state names are single uppercase
letters.
For example, given the
state machine description and the information that the initial state is `C':
|
A B C B A A C A D D D C |
We can draw a
picture of the state machine as shown below.
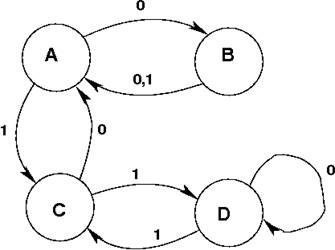
Figure 1 State Machine Diagram
Sample input and
output is:
|
Interface |
Comment: Input or Output |
|
C |
Output |
|
0 |
Input |
|
A |
Output |
|
0 |
Input |
|
B |
Output |
|
c 0 C |
Input |
|
0 |
Input |
|
C |
Output |
|
p |
Input |
|
A B C B C A C A D D D C |
Output |
|
g |
Input |
|
No Garbage |
Output |
|
c 1 B |
Input |
|
g |
Input |
|
Garbage: D |
Output |
|
d |
Input |
|
Deleted: D |
Output |
|
p |
Input |
|
A B C B C A C A B |
Output |
Submit your lab
1. Go to your coe428 directory
2. Zip your lab4 directory by using the following command:
zip -r lab4.zip lab4/
3. Submit the lab4.zip file using the following command:
submit
coe428 lab4 lab4.zip
by Ken
Clowes, revised by Ivan Lee, revised by Olivia Das